Java 集合实现了常用数据结构,是开发中最常用的功能之一。
Java 集合主要的功能由三个接口:List、Set、Queue 以及 Collection 组成。
常见接口:
- List : 列表,顺序存储,可重复
- Set :集合,与数学中的集合有同样的特性:元素不能重复
- Queue:队列
- Collection:所有 Java 集合的接口,定义了“集合”的常用接口
结构结构
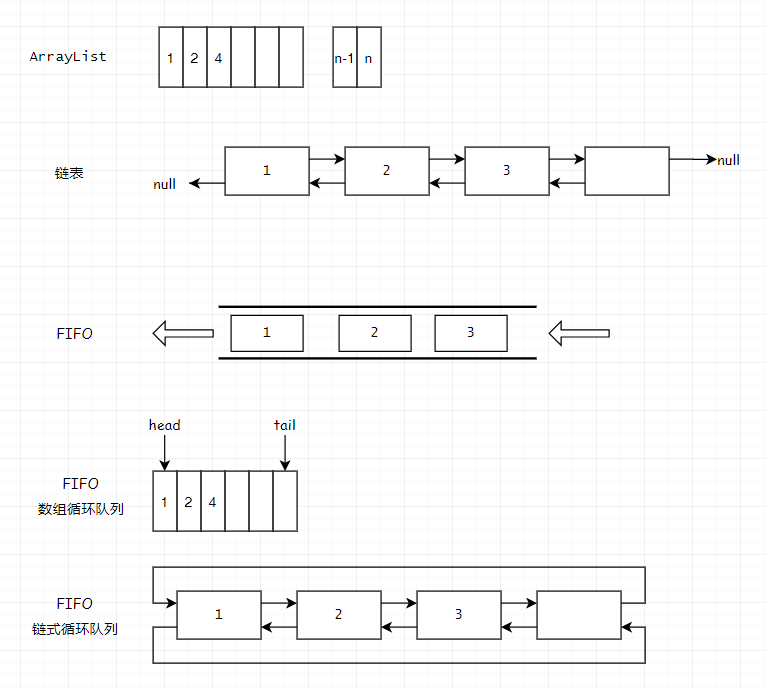
常用集合
- ArrayList 一种可以动态增长或缩减的索引集合,底层通过
Ojbect[]数组实现,默认容量为 10,在使用是如果确定仓储的数据容量应尽量为其初始化以避免动态扩容时的拷贝开销 - LinkedList 高效插入删除的有序序列,是双向链表,使用 node 节点存储数据;它又实现了双向队列
- ArrayDeque 用循环数组实现的双端队列
- HashSet 一种没有元素的无序集合
- TreeSet 有序的集合
- LinkedHashSet 能记录插入顺序的集合
- PriorityQueue 优先队列
- HashMap 存储键/值关系数据
- TreeMap 能根据键的值排序的键/值关系数据数据
- LinkedHashMap 可以键/值记录添加顺序
Java 集合框架结构
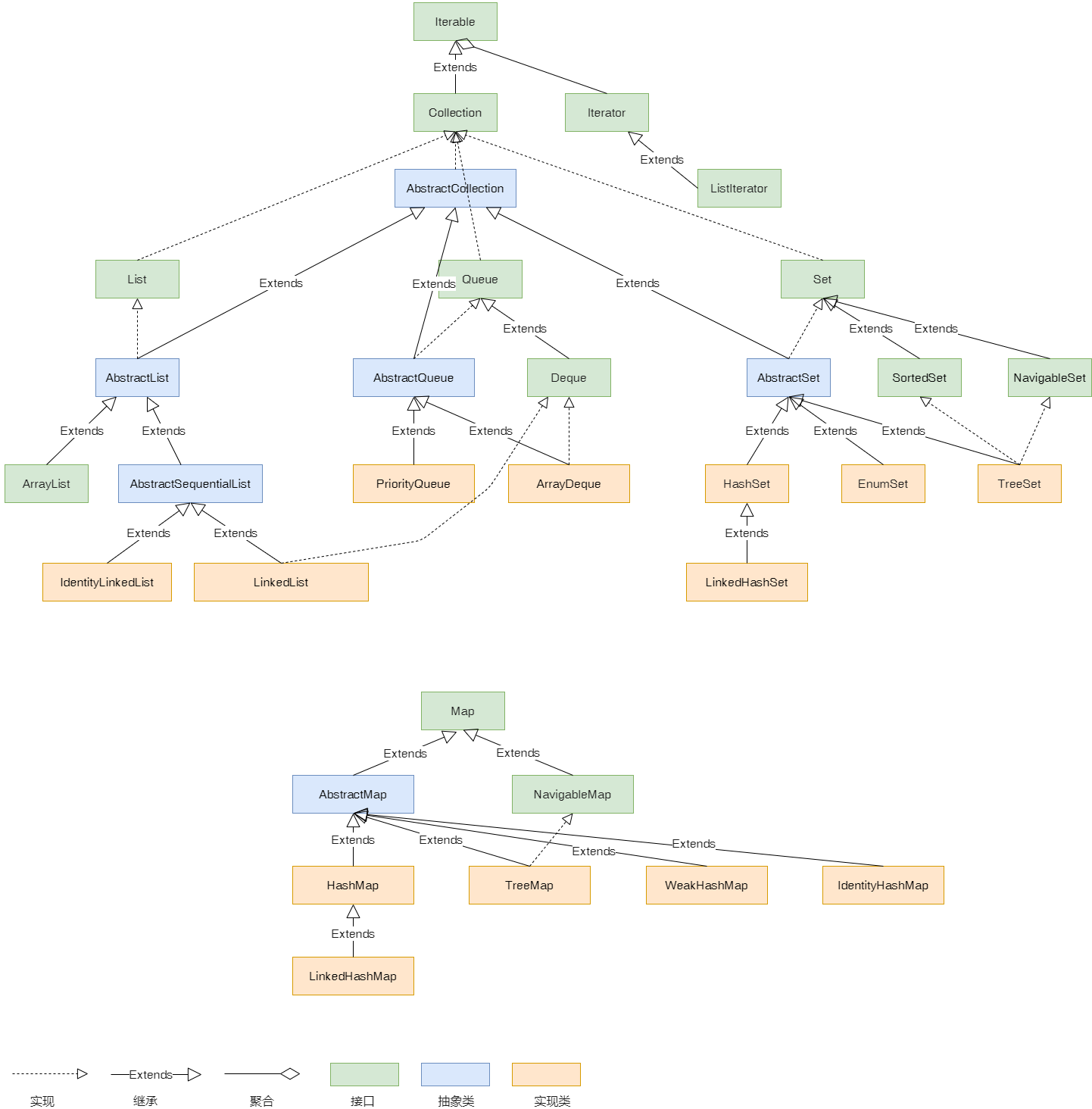
如何选用这些数据结构
通常选用基于我们需要处理的数据的特点以及集合的特点来确定的。
如果只是简单存储一组数据,如几个用户的信息,这时选用 ArrayList 是比较合适的,如果数据频繁添加、删除那选用 LinkedList 是比较合适的。
如果想存储一组数据且不希望重复,那选用 Set 集合合适的。
如果希望添加插入的数据能够有顺序,那选择 TreeSet 是比较合适的,当然 TreeMap 也可以。
使用
ArrayList
1import org.junit.Test;
2
3import java.util.ArrayList;
4import java.util.Arrays;
5import java.util.Collections;
6import java.util.List;
7
8public class ArrayListTest {
9
10 @Test
11 public void test() throws Exception {
12 ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
13 // 更推荐使用面向接口的使用方式,方便以后切换
14 //List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
15 list.add(3);
16 list.add(2);
17 list.add(1);
18
19 // for打印
20 for (Integer e : list) {
21 System.out.println(e);
22 }
23
24 // 排序 小->大
25 Collections.sort(list);
26 System.out.println(list); // 打印
27
28 // 排序 大->小
29 List<Integer> list2 = Arrays.asList(2,3,5);
30 Collections.sort(list2,(a,b)->b-a);
31
32 // 排序 大->小
33 list2.sort((a, b) -> b - a); // 功能同上
34 System.out.println(list2);
35 }
36}
37// 输出
383
392
401
41[1, 2, 3]
42[5, 3, 2]
Set
1import org.junit.Test;
2
3import java.util.HashSet;
4import java.util.Objects;
5import java.util.Set;
6
7public class SetTest {
8
9 static class User {
10 String name;
11 int age;
12
13 public User(String name, int age) {
14 this.name = name;
15 this.age = age;
16 }
17
18 @Override
19 public int hashCode() {
20 return Objects.hashCode(this.name);
21 }
22
23 // 逻辑根据名字判断User是否相同
24 @Override
25 public boolean equals(Object obj) {
26 if (obj == null) return false;
27 if (obj instanceof User) {
28 User u = (User) obj;
29 return this.name != null
30 ? this.name.equals(u.name)
31 : u.name == null;
32 }
33 return false;
34 }
35
36 @Override
37 public String toString() {
38 return "User{" +
39 "name='" + name + '\'' +
40 ", age=" + age +
41 '}';
42 }
43 }
44
45
46 @Test
47 public void test() throws Exception {
48 Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
49 set.add(1);
50 set.add(2);
51 set.add(3);
52 set.add(3);
53 System.out.println(set);
54
55 // 添加重复的人
56 Set<User> users = new HashSet<>();
57 users.add(new User("张三",18));
58 // 重复,不进行添加
59 users.add(new User("张三",19));
60 users.add(new User("李四",20));
61 for (User u : users) {
62 System.out.println(u);
63 }
64 }
65}
66
67// 输出
68[1, 2, 3]
69User{name='null', age=18}
70User{name='李四', age=20}
HashMap
1import org.junit.Test;
2
3import java.util.HashMap;
4import java.util.Map;
5
6public class HashMapTest {
7 @Test
8 public void test() throws Exception {
9 HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
10
11 map.put("张三","110");
12 map.put("李四","119");
13 map.put("王二","120");
14 // 键重复,更新原有的
15 map.put("王二","139");
16
17 for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
18 System.out.println(entry.getKey()+" ---> "+entry.getValue());
19 }
20 }
21}
22// 打印
23李四 ---> 119
24张三 ---> 110
25王二 ---> 139
源码分析
基于 JDK1.8。
不重要的方法已经清除,保留的方法已经注释。
ArrayList
1package java.util;
2
3import java.util.function.Consumer;
4import java.util.function.Predicate;
5import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
6import sun.misc.SharedSecrets;
7
8public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
9{
10 /**
11 * 默认容量
12 */
13 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
14
15 /**
16 * 空数组,用作初始化
17 */
18 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
19
20 /**
21 * 共享空数组
22 */
23 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
24
25 /**
26 * 存放数据数
27 */
28 transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
29
30 /**
31 * 数组大小,elementData存储元素数量同步
32 */
33 private int size;
34
35 /**
36 * 构造器
37 */
38 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
39 if (initialCapacity > 0) {
40 this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
41 } else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
42 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
43 } else { // inittialCapatity < 0 抛出异常
44 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
45 initialCapacity);
46 }
47 }
48
49 /**
50 * 构造器
51 */
52 public ArrayList() {
53 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
54 }
55
56 /**
57 * 构造器
58 */
59 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
60 elementData = c.toArray(); // c!= null
61 if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
62 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
63 // 不是一个一个取值赋值给elementData,copyOf使用System.arrayCopy(), arrayCopy使用本地方法(JNI)效率很高
64 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
65 } else {
66 // replace with empty array.
67 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
68 }
69 }
70
71 /**
72 * 去掉数组(elementData)中不存数据的部分
73 */
74 public void trimToSize() {
75 modCount++;
76 if (size < elementData.length) {
77 elementData = (size == 0)
78 ? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
79 : Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
80 }
81 }
82
83 /**
84 * 调整List大小,可以扩容和缩容,缩容时最小容量不小于10
85 */
86 public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
87 int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
88 ? 0
89 : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
90
91 // 小于最小容量不调整,因此最小容量不会小于10
92 if (minCapacity > minExpand) {
93 ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
94 }
95 }
96
97 /**
98 * 最大容量
99 */
100 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
101
102 /**
103 * 动态扩容方法, 容量为之前的1.5倍 oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)
104 */
105 private void grow(int minCapacity) {
106 // overflow-conscious code
107 int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
108 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
109 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
110 newCapacity = minCapacity;
111 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
112 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
113 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
114 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
115 }
116
117 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
118 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
119 throw new OutOfMemoryError();
120 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
121 Integer.MAX_VALUE :
122 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
123 }
124
125 /**
126 * 获取list大小
127 */
128 public int size() {
129 return size;
130 }
131
132 /**
133 * 判断list是否为空
134 */
135 public boolean isEmpty() {
136 return size == 0;
137 }
138
139 // 每次取出元素操作时都会调用此方法对Ojbect数组原型进行类型转换
140 E elementData(int index) {
141 return (E) elementData[index];
142 }
143
144 /**
145 * 获取元素
146 */
147 public E get(int index) {
148 rangeCheck(index); // 检查是否越界
149 return elementData(index);
150 }
151
152 /**
153 * 添加元素
154 */
155 public boolean add(E e) {
156 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
157 elementData[size++] = e;
158 return true;
159 }
160
161 /**
162 * 删除
163 */
164 public E remove(int index) {
165 rangeCheck(index);
166 modCount++;
167 E oldValue = elementData(index);
168 int numMoved = size - index - 1;
169 if (numMoved > 0)
170 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
171 numMoved);
172 elementData[--size] = null;
173 return oldValue;
174 }
175
176 /**
177 * 两个list做差集
178 */
179 public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
180 Objects.requireNonNull(c);
181 return batchRemove(c, true);
182 }
183
184 /**
185 * 批量移除
186 */
187 private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {
188 final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;
189 int r = 0, w = 0;
190 boolean modified = false;
191 try {
192 for (; r < size; r++)
193 if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)
194 elementData[w++] = elementData[r];
195 } finally {
196 if (r != size) {
197 System.arraycopy(elementData, r,
198 elementData, w,
199 size - r);
200 w += size - r;
201 }
202 if (w != size) {
203 // clear to let GC do its work
204 for (int i = w; i < size; i++)
205 elementData[i] = null;
206 modCount += size - w;
207 size = w;
208 modified = true;
209 }
210 }
211 return modified;
212 }
213
214 @Override
215 public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
216 Objects.requireNonNull(action);
217 final int expectedModCount = modCount;
218 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
219 final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData;
220 final int size = this.size;
221 for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
222 // 调用回调 (e)->{ //操作e }
223 action.accept(elementData[i]);
224 }
225 // 遍历过程禁止修改list!
226 if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
227 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
228 }
229 }
230
231 /**
232 * 移除步骤:
233 * 1. 标记移除
234 * 2. 修改线程
235 * 3. 移动元素
236 * 4. 清除尾部元素
237 */
238 @Override
239 public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
240 Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
241
242 int removeCount = 0;
243 final BitSet removeSet = new BitSet(size);
244 final int expectedModCount = modCount;
245 final int size = this.size;
246 // 标记元素
247 for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < size; i++) {
248 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
249 final E element = (E) elementData[i];
250 if (filter.test(element)) {
251 removeSet.set(i);
252 removeCount++;
253 }
254 }
255 if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
256 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
257 }
258 // shift surviving elements left over the spaces left by removed elements
259 final boolean anyToRemove = removeCount > 0;
260 if (anyToRemove) {
261 final int newSize = size - removeCount;
262 // 移动元素 例如: [1][2][3] size=2 移动后 [1][3][3]
263 for (int i=0, j=0; (i < size) && (j < newSize); i++, j++) {
264 i = removeSet.nextClearBit(i);
265 elementData[j] = elementData[i];
266 }
267 // 清除尾部元素
268 for (int k=newSize; k < size; k++) {
269 elementData[k] = null; // Let gc do its work
270 }
271 // 更新size
272 this.size = newSize;
273 if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
274 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
275 }
276 modCount++;
277 }
278 return anyToRemove;
279 }
280}
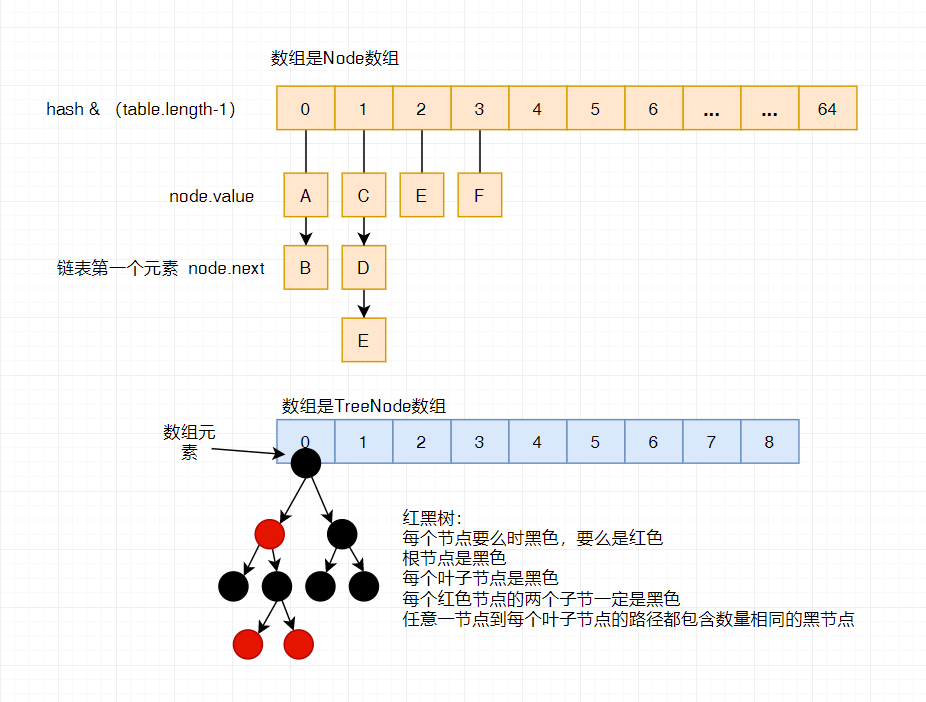
HashMap
底层数据结构:数组链表+红黑树
默认的容量为:16(1«4)
扩容的条件:size>=容量*加载因子
扩容大小:旧容量 2 倍(newCap = oldCap « 1)
树化(terrify)的条件
- 容量长度大于等于 64
- 链表成都大于 8
树化的过程
- 把普通节点转换为 TreeNode
- 调用 treeify 进行树化
- 调整节点
- 左旋右旋
put 导致死循环的原因。在 JDK1.7 中插入元素使用头插法,插入的时候不需要遍历哈希桶,在多线程下这样可能形成循环链表。JDK8 采用尾插法,循环找到最后一个节点,然后在最后一个节点插入元素。
存储结构
1public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
2
3 /**
4 * 默认容量16
5 */
6 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
7
8 /**
9 * 最大容量,1 << 30 = 1073741824
10 */
11 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
12
13 /**
14 * 默认加载因子,是决定存储容量扩容的关键指标,计算公式: size/总容量
15 */
16 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
17
18 /**
19 * 小于这个值无法使用红黑树,HashMap容量不推荐为奇数,比这个数小后树退化为数组
20 * 红黑树扩展时也参考这个属性
21 */
22 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
23
24 /**
25 * 容量小于这个值红黑树将退化为数组存储
26 */
27 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
28
29 /**
30 * 将数组转化为红黑树推荐的容量
31 */
32 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
33
34 /**
35 * 使用数组存储的数据结构,node节点
36 */
37 static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
38 final int hash;
39 final K key;
40 V value;
41 Node<K,V> next;
42
43 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
44 this.hash = hash;
45 this.key = key;
46 this.value = value;
47 this.next = next;
48 }
49 }
50
51 /**
52 * 计算对象的hash值,是hash code分配更均匀,减少冲突几率
53 */
54 static final int hash(Object key) {
55 int h;
56 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
57 }
58
59 /**
60 * 计算2的幂次方表容量
61 * 也就是说表容量只能为: ... 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 ... 1024 ... 1073741824
62 */
63 static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
64 int n = cap - 1;
65 n |= n >>> 1;
66 n |= n >>> 2;
67 n |= n >>> 4;
68 n |= n >>> 8;
69 n |= n >>> 16;
70 return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
71 }
72
73 /* ---------------- Fields -------------- */
74
75 /**
76 * 数组存储结构,默认第一次使用时会分配空间
77 */
78 transient Node<K,V>[] table;
79
80 /**
81 * 键值对数量
82 */
83 transient int size;
84
85 /**
86 * 对table修改的次数,调整table时改变 —— rehash、remove、add等操作
87 * 用来判断在读取操作过程中是否出现table修改
88 */
89 transient int modCount;
90
91 /**
92 * 扩容时的临界值,计算为 capacity*loadFactor
93 */
94 int threshold;
95
96 /**
97 * 加载因子, 默认0.75
98 */
99 final float loadFactor;
100
101 /* ---------------- Public operations -------------- */
102
103 /**
104 * 默认构造函数,table容量为16
105 */
106 public HashMap() {
107 this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // 0.75
108 }
109
110 /**
111 * 获取存储键值对数量
112 */
113 public int size() {
114 return size;
115 }
116
117 /**
118 * 判空
119 */
120 public boolean isEmpty() {
121 return size == 0;
122 }
123
124 /**
125 * 通过key获取value
126 * 下面的getNode是核心方法。
127 */
128 public V get(Object key) {
129 Node<K,V> e;
130 return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
131 }
132
133 /**
134 * 获取操作
135 */
136 final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
137 Node<K,V>[] tab;
138 Node<K,V> first, e;
139 int n; // n table长度
140 K k;
141
142 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
143 if (first.hash == hash && ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
144 return first;
145 if ((e = first.next) != null) {
146 // 根据存储结构来获取数据
147
148 // 红黑树,调用getTreeNode
149 if (first instanceof TreeNode)
150 return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
151
152 // 遍历链表
153 do {
154 //较key查询value
155 if (e.hash == hash &&
156 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
157 return e;
158 } while ((e = e.next) != null);
159 }
160 }
161 return null;
162 }
163
164 /**
165 * 添加数据
166 */
167 public V put(K key, V value) {
168 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
169 }
170
171 /**
172 * Implements Map.put and related methods.
173 *
174 * @param hash hash for key
175 * @param key the key
176 * @param value the value to put
177 * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
178 * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
179 */
180 final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
181 boolean evict) {
182 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
183
184 // table未初始化会执行
185 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
186 n = (tab = resize()).length;
187
188 // 存放值
189 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)// 判断通过hash计算出的位置是否有值
190 // 没有就在该位置(i)创建一个node并赋值
191 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
192 else {// 这里时计算出的位置有值存在
193 Node<K,V> e; K k;
194
195 if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
196 // 判断hash值、key相同,认为
197 e = p;
198 else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
199 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
200 else {
201 // 遍历哈希桶
202 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
203 // 遍历到桶最后一个元素(链表最后一个元素)
204 if ((e = p.next) == null) {
205 // 添加元素
206 p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
207 // 判断,只有哈希桶至少为8个的时候才进行树化,TREEIFY_THRESHOLD默认为8
208 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
209 treeifyBin(tab, hash);
210 break;
211 }
212 // 判断键值是否相同
213 if (e.hash == hash &&
214 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
215 break;
216 // 下一个元素
217 p = e;
218 }
219 }
220
221 // 更新值
222 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key —— 存在键的映射
223 V oldValue = e.value;
224 if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
225 e.value = value;
226 afterNodeAccess(e);
227 return oldValue;
228 }
229 }
230 ++modCount;
231 // 超出HashMap存放元素的阈值threshold = capacity * loadFactor(0.75)
232 if (++size > threshold)
233 // 调整Hash存在空间大小
234 resize();
235 afterNodeInsertion(evict);
236 return null;
237 }
238
239 /**
240 * Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
241 * accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
242 * Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
243 * elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
244 * with a power of two offset in the new table.
245 *
246 * @return the table
247 */
248 final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
249 Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
250 // 旧容量,为哈希桶长度
251 int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
252 int oldThr = threshold;
253 int newCap, newThr = 0;
254 // 这个if用来保证HashMap阈值threshold不超限
255 if (oldCap > 0) {
256 // 判断是否超出最大容量,到最大容量不再扩容
257 if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
258 // 阈值设置整型最大值
259 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
260 // 返回并不再调整大小
261 return oldTab;
262 }
263 // 在容量范围内
264 else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
265 oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
266 newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 为原先的两倍
267 }
268 else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
269 newCap = oldThr;
270 else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
271 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
272 newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
273 }
274
275 // 计算加载因子,设置新的阈值 阈值=新容量*加载因子
276 if (newThr == 0) {
277 float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
278 newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
279 (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
280 }
281 threshold = newThr;
282 // 新的哈希桶
283 @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
284 Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
285 table = newTab;
286 // 将旧桶的元素更新到新桶
287 if (oldTab != null) {
288 for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
289 Node<K,V> e;
290 if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
291 oldTab[j] = null;
292 if (e.next == null)
293 // 旧桶中的值移动到新桶
294 newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
295 else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
296 // 执行红黑树操作
297 ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
298 else { // preserve order - 翻转顺序
299 Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
300 Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
301 Node<K,V> next;
302 do {
303 next = e.next;
304 if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
305 if (loTail == null)
306 loHead = e;
307 else
308 loTail.next = e;
309 loTail = e;
310 }
311 else {
312 if (hiTail == null)
313 hiHead = e;
314 else
315 hiTail.next = e;
316 hiTail = e;
317 }
318 } while ((e = next) != null);
319 if (loTail != null) {
320 loTail.next = null;
321 newTab[j] = loHead;
322 }
323 if (hiTail != null) {
324 hiTail.next = null;
325 newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
326 }
327 }
328 }
329 }
330 }
331 return newTab;
332 }
333
334 /**
335 * 树化方法
336 * Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless
337 * table is too small, in which case resizes instead.
338 */
339 final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
340 int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
341 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
342 resize();
343 else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
344 TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
345 do {
346 TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
347 if (tl == null)
348 hd = p;
349 else {
350 p.prev = tl;
351 tl.next = p;
352 }
353 tl = p;
354 } while ((e = e.next) != null);
355 if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
356 hd.treeify(tab);
357 }
358 }
359
360 /* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
361 // Tree bins
362
363 /**
364 * 红黑树
365 *
366 * Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn
367 * extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or
368 * linked node.
369 */
370 static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
371 TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
372 TreeNode<K,V> left;
373 TreeNode<K,V> right;
374 TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
375 boolean red;
376 TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
377 super(hash, key, val, next);
378 }
379 }
380}
(完)